Cerebral blood flow is the blood supply to the brain in a given period of time. The term meridian describes the overall energy distribution system of Chinese Medicine and.
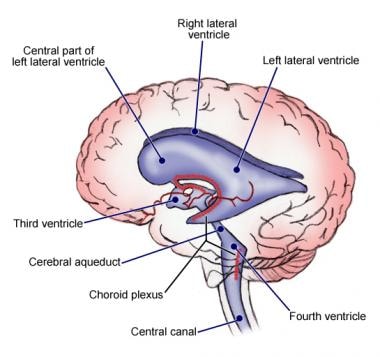
Ventricles Of The Brain Overview Gross Anatomy Microscopic Anatomy
Cerebral blood flow is tightly regulated to meet the brains metabolic demands.

. Color is from myelin sheaths. Its function remained unclear until CSF circulation was theorized during the nineteenth century 2 17. Up to 24 cash back Directional Terms and Landmarks.
The interthalamic adhesion is a mass of grey matter that travels through the third ventricle and connects the 2 thalami may be absent in some individuals. The metencephalon develops into the pons and part of the medulla oblongata cerebellum and. The mesencephalon develops into the tectum corpora quadrigemina cerebral peduncles and cerebral aqueduct.
Ventricles subarachnoid space of the brain and spinal cord and the central canal of the spinal cord. A new directional term associated with the head. Between the pia mater the the arachnoid mater.
The cerebral aqueduct Sylvian aqueduct or aqueduct of Sylvius exits the third ventricle at its posteroinferior aspect allowing the third ventricle to communicate with the fourth ventricle. It is a symmetrical structure situated on top of the brain stem and on either side of. The PVS has also been found on the arachnoid mater cerebellum perinervium and epinervium of the sciatic nerve.
Runs through the midbrain and connects the third and fourth ventricles. The cerebral cortex of the human brain is highly convoluted meaning it has many folds and creases. The PVs and PNs flow in the third ventricle fourth ventricle cerebral aqueduct and along the central canal of the spinal cord.
Describe the process of clonal selection. The corpora quadrigemina are the four colliculitwo inferior two superiorlocated on the tectum of the dorsal aspect of the midbrain. Cerebral aqueduct Fourth ventricle Cerebellum a Anterior Epithalamus commissure Temporal lobe Medulla oblongata Figure 142a.
CSF fills subarachnoid space and bathes external surfaces of brain and spinal cord. Describe the structures of the cerebral hemispheres including the lobs of the brain and their components using the whole-brain and midsagittally sectioned specimens. Explain the directional terms associated with the orientation of the brain in the cranial cavity.
What are the embryological terms used to describe direction in the brain. The thalamus is located deep within the brain in the cerebral cortex adjacent to the hypothalamus. The diameter of the Cerebral Aqueduct is too small to accommodate the choroid plexus.
In an adult cerebral blood flow is typically 750 milliliters per minute or 15 of the cardiac output. As more information arose about the anatomy of the brain anatomists described the cerebral aqueduct as a narrow communication duct between the third and fourth ventricles. You may also use anterior in.
In this technique two gradient-echo images are produced. Galen initially described the ventricular system of the brain. The word aqueduct comes from the Latin word aqueductus which translates to a canal used for taking water through a structure.
CSF flows out Median and Lateral Apertures or through Central Canal of Spinal Cord. Anterior Posterior front back Rostral Caudal towards the beak towards the tail Medial Lateral towards the middle towards the side Dorsal Ventral top bottom on the CNS of a quadruped Superior Inferior on top of underneath Frontal or Coronal section parallel to rostralcaudal axis. Beneath the arachnoid mater in the subarachnoid space ie.
CSF flows down cerebral aqueduct to fourth ventricle. Identify the passageway found in the spinal cord that is continuous with the ventricles. Cerebrospinal fluid circulates through a system of cavities found within the brain and spinal cord.
The canal that passes through midbrain - canal aqueduct. Describe the structures of the cerebral hemispheres including the lobs of the brain and their components using the whole-brain and midsagittally sectioned tissue. Describe the layers of tissue that cover the brain and explain their function.
What nonlymphocyte cell is a central actor in this process and what is its. The great majority of cerebral commissural tracts pass through the ____ _____. Here the fluid scapes via the lateral apertures of the fourth ventricle and the medial foramen of the fourth ventricle into.
No cell bodies but millions of axons present. The aqueduct is the residue of the primitive mesencephalic cavity and its shape varies from the. Arterial blood flow and CSF flow in the cerebral aqueduct were quantified using quantitative single-slice PC angiography PCA.
The umbilical cord is _____ to the appendages. 14-33 Cerebrum - Gross Anatomy two cerebral hemispheres divided by longitudinal fissure. The CSF is formed in the lateral ventricles circulates through the interventricular foramens into the third ventricle and then via the cerebral aqueduct into the fourth ventricle.
Fundamental Neuroscience for Basic and Clinical Applications Fifth Edition 2018. Although transverse is a directional term. Cerebrospinal fluid CSF is a clear colorless plasma-like fluid that bathes the central nervous system CNS.
With regard to directional terms often used to describe brain anatomy the term _____ means toward the tail while the term _____ means toward the nose. In terms of the meninges where do the cerebral arteries run. Explain the directional terms associated with the orientation of the brain in the cranial cavity.
From the choroid plexus the CSF flows to the lateral ventricle then to the interventricular foramen of Monro the third. Cerebral Spinal Fluid CSF flows through the ventricles or interconnecting spaces of the brain. Circulation of the Cerebrospinal Fluid.
Choroid plexus in the fourth ventricle adds more CSF. Normal route of CSF from production to clearance is the following. - small triangular chamber between pons and cerebellum.
Describe human embryo development. Central Nervous System Chapter 13 matter present in the brain. Describe the layers of tissue that cover the brain and explain their function.
Cerebrospinal fluid flow. Choose the best directional term for the following statement. CSF circulation begins in the Lateral Ventricles which are deep within each cerebral hemisphere.
The cerebral aqueduct was first illustrated by Leonardo da Vinci but it was named after Francois Sylvius de la Boe 16141672 an anatomy professor at Leyden. Cerebral aqueduct 5 fourth ventricle. Single narrow medial space beneath corpus callosum.
The cerebral aqueduct is a narrow channel 1 to 3 mm in diameter that connects the third ventricle the cavity of the diencephalon with the fourth ventricle the rhombencephalic cavity. The following directional terms. Cerebral aqueduct - canal that passes through midbrain.
External to internal gray matter. A flow-sensitive image using a pair of matched directional gradients and a flow-insensitive image using a pair of matched bipolar gradients.

Ventricles Of The Brain Labeled Anatomy Function Csf Flow Definition Ezmed

Ventricles Of The Brain Labeled Anatomy Function Csf Flow Definition Ezmed

Ventricles Of The Brain Labeled Anatomy Function Csf Flow Definition Ezmed
0 Comments